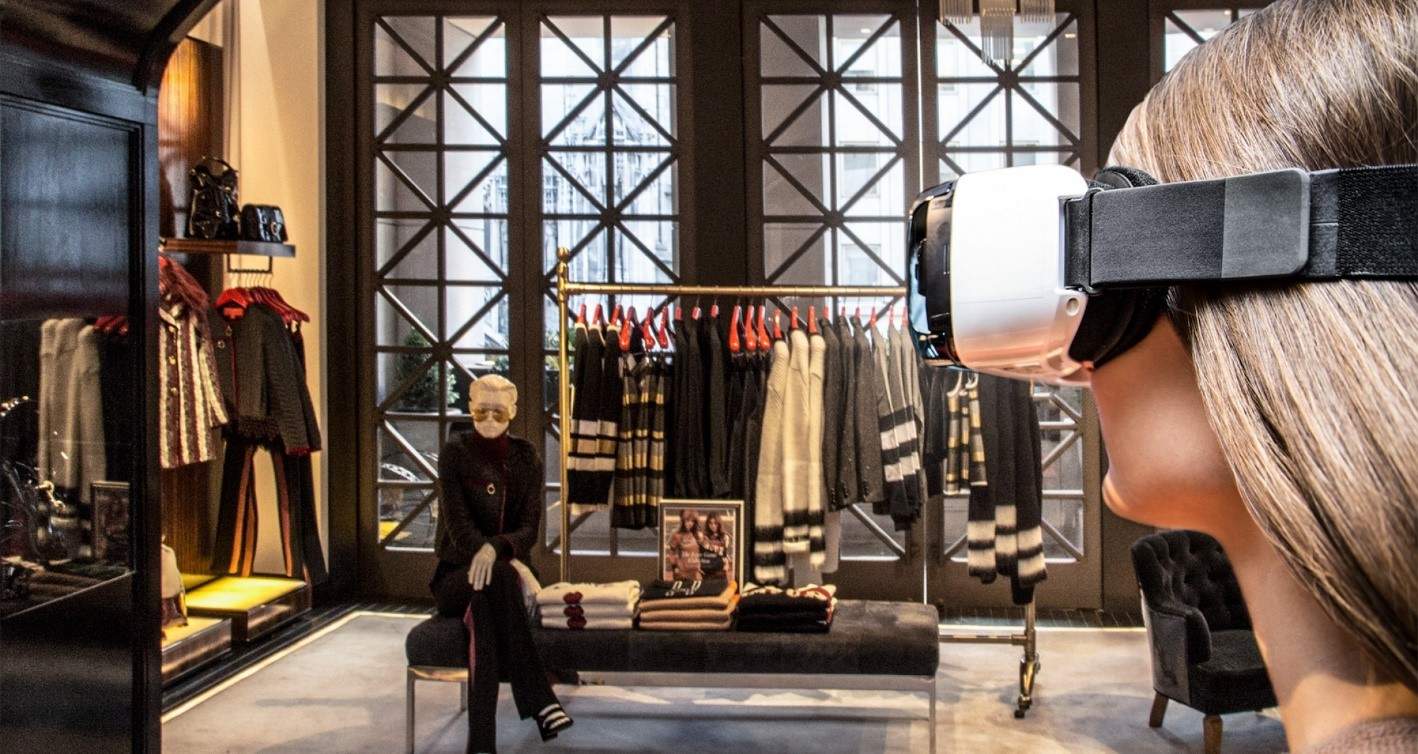
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies have the ability to transform numerous industries, including fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), retail, and foodservice by creating new ways of marketing to improve consumer experience. Technology companies are regularly working on expanding the VR ecosystem, while trying to develop sustainable AR ecosystems to gain a foothold in the lucrative market.
Technology Trends
Listed below are the key technology trends impacting VR and AR, as identified by GlobalData.
AR as the next big computing platform
AR could be the next big computing platform. Users could eventually be wearing a pair of glasses with the computing power of a smartphone, activated by their voice, which recognises what they see, where they are, and the context in which they are operating.
5G
The bandwidth limitations of current telecom networks are a major factor restricting AR’s growth. The first 5G devices are starting to hit the shelves in some countries. Samsung’s Galaxy S10 5G smartphone, launched in February 2019, promises graphic-rich AR with minimal latency issues. Qualcomm, in collaboration with Acer, LG, and Sprint, has plans to bring phone-powered AR headsets with 5G network capabilities to the market by the end of 2019.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
The growing pervasiveness of AI techniques across the expanding breadth of VR applications is enhancing the intelligence of virtual characters and delivering a rich immersive environment. AI’s impact on VR can be gauged from recent developments. For example, Google’s machine learning tools add 6DoF controller-tracking capabilities to any standalone headset with a pair of cameras, while Facebook’s DeepFocus framework uses AI to create focus effects in VR that mirror real life, and LG is using AI to minimise motion sickness for VR users.
Machine learning (ML)
ML is an application of AI that gives computer systems the ability to learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed. AR apps can use ML systems to improve their user experience (UX) by continually analysing user activities. Apple’s CoreML 3, which powers the ARKit 3, enables developers to run ML models on iOS devices, improving object recognition in photos and gesture recognition.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataEye tracking and facial recognition, which are fast becoming standard functions across all AR hardware platforms, typically use ML systems to continually improve UX. As mobile AR develops, there will be a greater demand for ML systems to be smaller, faster, and more accurate.
Conversational platforms
Smartphones today typically come with virtual assistants integrated into the operating system. AR headsets and smart glasses are beginning to incorporate similar capabilities. Microsoft’s Cortana in HoloLens 2, Amazon’s Alexa in Focals by North, and Google Assistant in Bose AR smart glasses are just a few of the early iterations of voice capable AR devices.
Facebook introduced Oculus Voice in 2017, but the service was basic, with just four commands. The limited functionality meant Oculus Voice suffered in comparison to popular virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Google’s Assistant.
AR cloud
AR cloud refers to a real-time 3D virtual map overlaid onto the real world. It allows multiple users and devices to share AR experiences. In the jargon, AR cloud promises to enable persistent content for use by multiple users, either individually or collectively.
For example, AR cloud technology can create an indoor navigation system for a retail outlet, allowing customers to be guided along a virtual path to all products on a supermarket’s shelves, providing the customer nutritional data, thereby saving the customer’s time to find what is needed.
Google, Apple, Microsoft, Facebook, Amazon, Magic Leap, Samsung, and Niantic are all heavy investors in AR cloud. Google introduced an update to ARCore that allows users to generate, share, and save persistent AR content in public places for multi-user experiences.
Integration of cloud and VR
Cloud technologies promise scalability to VR vendors. Low latency, frictionless cloud-native apps will improve customer satisfaction with fresh VR updates. Today’s cloud market leaders – Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and IBM – are expected to benefit from the integration of cloud and VR in the coming years as VR companies will increasingly subscribe to their cloud services.
Data visualisation
Data visualisation is an emerging enterprise use case for AR. IBM, in 2019, introduced Immersive Data for iOS, an AR visualisation tool that allows scientists and executives to visualise data in interactive 3D formats.
Contact lenses
AR-capable contact lenses are being developed and could turn AR into a more natural, intuitive, and accessible utility. Samsung gained an AR contact lens patent in 2016, with Sony moving into the same area in 2017. Microsoft is also reportedly investing $2m in this technology, while start-up firm Mojo Vision has raised more than $100m in funding for microdisplay technology that could potentially be used in contact lenses.
Occlusion
Occlusion is a major issue for AR developers, as virtual objects can become hidden behind real things. Most AR systems currently lack depth-sensing capabilities that would allow the devices’ cameras to accurately locate the position of a real object in 3D space and ensure that virtual objects were placed in plain sight.
However, several initiatives are underway to tackle the occlusion issue. Apple, for instance, introduced People Occlusion in ARKit 3, which allows virtual objects to appear in front of or behind people.
AR payments
AR is entering the fintech sector by enabling frictionless payments. Start-up Curve is working on an AR-based payment system, while PayPal is working on smart glass-based AR payments, and Ant Financial’s Alipay mobile payments app already has the AR functionality.
VR app development
VR apps are proving increasingly popular. In 2019, VRChat boasted of more than 10,000 daily peak concurrent users, while at the time of writing Astro Bot Rescue Mission had over 58,000 watch hours on Steam. Beat Saber became the first VR game to record sales of over a million copies, while Google Earth and BigScreen VR became popular non-game VR apps.
Facebook accounts for the most premium apps on VR at the time of writing, while HTC is the only VR company with an app store subscription service, introduced in early 2019.
3D audio
The growing demand for untethered headsets, along with the inherent limitations of human eyes, have necessitated the synchronisation of visuals with 3D audio for a truly immersive experience. Established players in the 3D audio business, such as Dolby Labs, Panasonic, and 3D Sound Labs, are exploring new growth opportunities in the VR market.
This is an edited extract from the Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Consumer Goods – Thematic Research report produced by GlobalData Thematic Research.





